 SLEでプラニケル(ヒドロキシクロロキン)を使用している20歳女性患者の慢性的な結膜充血の鑑別は?
SLEでプラニケル(ヒドロキシクロロキン)を使用している20歳女性患者の慢性的な結膜充血の鑑別は?
日本語
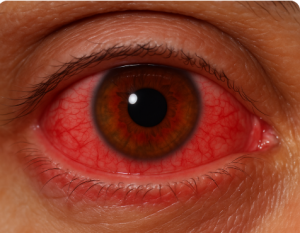
慢性的な結膜充血を認める場合、以下の原因が考えられます:
- 乾燥性角結膜炎(ドライアイ)
SLE患者では二次性シェーグレン症候群を合併することがあり、涙液分泌低下によって慢性的な結膜充血を生じます。 - 薬剤性影響(ヒドロキシクロロキン)
ヒドロキシクロロキンは主に網膜症や角膜沈着が知られていますが、まれに薬剤過敏反応の一部として結膜炎様症状を呈することがあります。 - アレルギー性結膜炎
若年者では季節性あるいは通年性アレルギーにより慢性的な充血が続くことがあります。 - 慢性炎症(SLE関連血管炎など)
ごくまれにSLEそのものによる血管炎や免疫学的炎症が結膜に影響し、慢性的な充血を呈することがあります。
English
In a patient with chronic conjunctival hyperemia while on hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), possible causes include:
- Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (Dry eye disease)
SLE may be associated with secondary Sjögren’s syndrome, leading to tear deficiency and chronic conjunctival redness. - Drug-related effects (Hydroxychloroquine)
Hydroxychloroquine is mainly associated with retinal toxicity and corneal deposits, but rarely may induce hypersensitivity reactions manifesting as conjunctivitis. - Allergic conjunctivitis
Common in young adults, either seasonal or perennial, and can present with chronic conjunctival redness. - Chronic inflammatory changes (SLE-related vasculitis, etc.)
Though uncommon, SLE-related vasculitis or immune-mediated inflammation may involve the conjunctiva and cause persistent redness.




コメント