ーー

 〇 米国眼科学会のビデオから、神経眼科の話題採録。2022年「神経眼科疾患の診断とマネジメント」です
〇 米国眼科学会のビデオから、神経眼科の話題採録。2022年「神経眼科疾患の診断とマネジメント」です
https://www.aao.org/annual-meeting-video/diagnosis-management-of-neuro-ophthalmic-disease-2
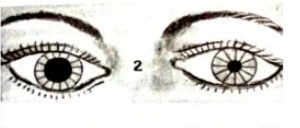
その中から重要なメッセージ:Hutchinson’s pupil
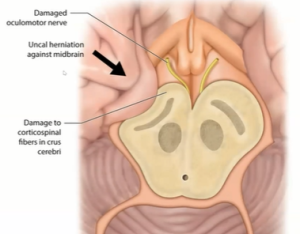
ハッチンソン瞳孔は、動眼神経の圧迫により、頭蓋内腫瘤病変の側の瞳孔が散大し、光に反応しない臨床徴候です。サインはジョナサン・ハッチンソン卿にちなんで名付けられました. これらは、脳への脳震盪損傷が原因である可能性があり、硬膜下出血および意識喪失に関連しています。瞳孔への副交感神経線維は、瞳孔収縮の原因です。繊維は動眼神経の末梢を通過するため、神経が圧迫された場合に最初に影響を受けます。ステージ 1 では、損傷側の副交感神経線維が刺激され、その側の瞳孔が収縮します。ステージ 2 では、損傷側の副交感神経線維が麻痺し、瞳孔が散大します。反対側の動眼神経の繊維が刺激され、反対側が収縮します。ステージ 3 では、両側の副交感神経線維が麻痺し、両側の瞳孔散大につながります。瞳孔は固定されます。これは重大な予後を示しています。
| Hutchinson’s pupil | |
|---|---|
Hutchinson’s pupil is a clinical sign in which the pupil on the side of an intracranial mass lesion is dilated and unreactive to light,[1] due to compression of the oculomotor nerve on that side. The sign is named after Sir Jonathan Hutchinson. These can be due to concussion injury to the brain and is associated with subdural haemorrhage and unconsciousness. The parasympathetic fibers to the pupil are responsible for pupillary constriction. The fibers pass through the periphery of the oculomotor nerve, and hence are the first to be affected in case of compression of the nerve. In Stage 1, the parasympathetic fibers on the side of injury are irritated, leading to constriction of pupil on that side. In stage 2, the parasympathetic fibers on the side of injury are paralysed, leading to dilatation of pupil. The fibers on the opposite oculomotor nerve are irritated, leading to constriction on opposite side. In stage 3, the parasympathetic fibers on both sides are paralysed – leading to bilateral pupillary dilatation. Pupils become fixed. This indicates grave prognosis.[citation needed]
注:
ハッチンソン徴候
ハッチンソン徴候は、以下を指す可能性 がある臨床徴候です。
- ハッチンソン瞳孔、頭蓋内腫瘤の側にある無反応で拡大した瞳孔
- 鼻の先端の水疱、または鼻の側面の水疱は、眼の帯状疱疹の発症に先行します。[1] これは、三叉神経の鼻毛枝が、鼻の先端だけでなく、角膜と鼻の外側背側の両方を神経支配するために発生します。このサインはジョナサン・ハッチンソン卿にちなんで名付けられました。[2]
- 近位の爪郭の色素沈着を伴うメラノキア。[3] : 671 これは、確実な予測因子ではありませんが、爪下黒色腫の重要な徴候です。爪周囲の色素沈着過剰は、少なくとも 1 つの非黒色腫皮膚がん、爪部のボーエン病で発生します。これは爪囲の色素沈着であり、その後徐々に広がり、関連する爪ジストロフィーを伴う三角形の色素沈着斑を生成します。爪床とマトリックスの色素沈着過剰は、ハッチンソン徴候をシミュレートする「透明な」爪囲を介して反映される可能性があります. [4]
- ハッチンソンのトライアド-先天性梅毒の症状のパターン。




コメント